vue-router和vuex入门
vue-router和vuex是官方提供的Vue插件,主要解决路由和状态管理两个问题
vue-router
基本概念
解决什么问题?vue-router解决了路由与组件的对应关系
vue-router的基本使用方法
- 安装vue-router依赖
npm i -S vue-router
- 使用vue-router插件
import Route from 'vue-router'
Vue.use(Route)
2
3
- 初始化vue-router对象
const routes = [
{ path: '/a', component: A },
{ path: '/b', component: B },
{ path: '/hello-world', component: HelloWorld }
]
const router = new Route({
routes
})
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
注:这里省略了定义A组件和B组件的过程,这两个组件与普通组件无异
- 实例化Vue对象,传入router参数
new Vue({
router,
render: h => h(App)
})
2
3
4
- 使用router-view和router-link
router-view和router-link是vue-router官方提供的两个组件,router-view会替换为路由对应的组件,router-link相当于a标签,点击后会加载to属性中路由对应的组件
<div>
<div>
<router-link to="/a">a</router-link>
</div>
<div>
<router-link to="/b">b</router-link>
</div>
<div>
<router-link to="/hello-world">hello-world</router-link>
</div>
</div>
<router-view />
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
路由嵌套
上面是一个非常简单的vue-router case,实际项目开发过程中,需求往往不会这么简单,比如我们希望实现/a/aa路由,并且/aa对应的组件嵌套在/a之下,这时我们需要修改路由的配置文件:
const routes = [{
path: '/a',
component: A,
redirect: '/a/aa',
children: [
{
path: '/a/aa',
component: AA,
}]
}]
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
并修改A组件的内容:
<template>
<div>
<div>a</div>
<router-view />
</div>
</template>
2
3
4
5
6
由于A组件是父级路由,所以也需要添加router-view组件,动态匹配子路由
重定向
将一个路由重定向到另一个路由,实际开发过程中非常实用,修改配置文件即可:
const routes = [{
path: '/a',
component: A,
redirect: '/a/aa',
children: [{
path: '/a/aa',
component: AA,
}]
}]
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
动态路由
为了支持restful形式路由以及更复杂的场景时,我们可以使用动态路由,定义路由时,在路由前加上冒号即可,我们先添加AA2组件,动态路由部分通过this.$route.params进行接收:
<template>
<div>
aa2
<div>{{id}}</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data() {
return {
id: null
}
},
created() {
this.id = this.$route.params.id
}
}
</script>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
修改路由配置后生效:
const routes = [
{
path: '/a',
component: A,
redirect: '/a/aa',
children: [
{
path: '/a/aa',
component: AA,
},
{
path: '/a/:id',
component: AA2,
},
]
}
]
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
动态路由的优先级低于普通路由,所以我们访问/a/aa时会匹配到AA组件,而输入其他路由时会匹配到AA2组件
路由参数
参数传递是我们开发过程中必不可少的步骤,vue-router支持参数传递,通过this.$route.query进行接收,我们修改AA组件进行测试
<template>
<div>
aa
<div>{{message}}</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data() {
return {
message: ''
}
},
created() {
this.message = this.$route.query.message || ''
}
}
</script>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
编程式路由
有很多时候我们需要手动操作路由的跳转,这时我们需要使用this.$router,以下是一些常用的操作:
- 路由跳转
this.$router.push('/a/aa')
- 带参数路由跳转
this.$router.push({
path: '/a/aa',
query: {
message: 'hello'
}
})
2
3
4
5
6
- 不向history插入记录
this.$router.replace('/a/123')
- 回退
this.$router.go(-1)
vuex
基本概念
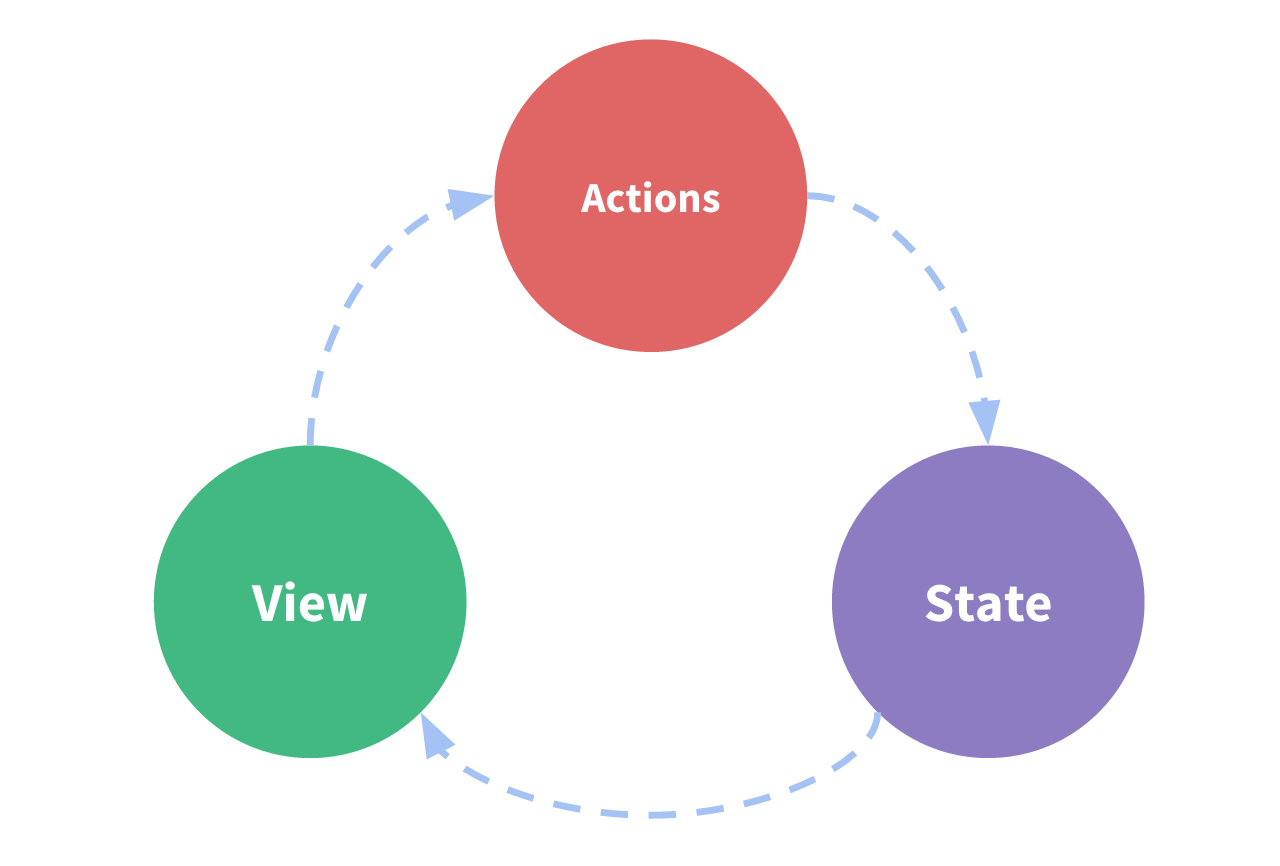
解决什么问题?vuex解决了状态管理问题,通过集中管理状态,使得state、action和view实现松耦合,从而让代码更易维护
vuex的基本使用方法
- 安装vuex依赖
npm i -S vuex
- 使用vuex插件
import Store from 'vuex'
Vue.use(Store)
2
3
- 初始化vuex对象
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state: {
data: 'this is data'
},
mutations: {
SET_DATA(state, data) {
state.data = data
}
},
actions: {
setData({ commit }, data) {
commit('SET_DATA', data)
}
}
})
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
- 实例化Vue对象,传入store参数
new Vue({
render: h => h(App),
router,
store
})
2
3
4
5
- 读取vuex状态
<div>{{$store.state.data}}</div>
- 更新vuex状态
update() {
this.$store.dispatch('setData', 'this is update data')
}
2
3
vuex模块化
实际项目开发中,状态众多,如果全部混在一起,则难以分辨,而且容易相互冲突,为了解决问题,vuex引入模块化的概念,解决这个问题,下面我们定义a和b两个模块:
const moduleA = {
state: {
data: 'this is a'
},
mutations: {
SET_DATA(state, data) {
state.data = data
}
},
actions: {
setData({ commit }, data) {
commit('SET_DATA', data)
}
}
}
const moduleB = {
state: {
data: 'this is b'
},
mutations: {
SET_DATA(state, data) {
state.data = data
}
},
actions: {
setData({ commit }, data) {
commit('SET_DATA', data)
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
修改store的初始化代码:
const store = new Vuex.Store({
modules: {
a: moduleA,
b: moduleB
}
})
2
3
4
5
6
修改获取状态的代码,此时需要加入模块进行区分:
<div>{{$store.state.a.data}}</div>
<div>{{$store.state.b.data}}</div>
<button @click="update('a')">update a</button>
<button @click="update('b')">update b</button>
2
3
4
修改update方法:
update(ns) {
this.$store.dispatch(`setData`, `update ${ns}`)
}
2
3
vuex命名空间
上述代码在执行过程中,获取状态没有问题,但是修改状态会出现问题,因为两个模块出现同名actions,所以此时需要使用命名空间来解决这个问题:
const moduleA = {
namespaced: true,
// ...
}
2
3
4
修改update方法:
update(ns) {
this.$store.dispatch(`${ns}/setData`, `update ${ns}`)
}
2
3